
The speed of the wave is determined by the properties which are physical in nature Of the material through which the wave will propagate. The wave field of the seismic waves is a fully elastic seismic wave field that propagates through isotropic earth which consists of a P-wave component and two shear wave components which are the SV and SH. Reflected P, SH, and SV signals can be generated which are needed to characterize the reservoirs and also to evaluate the prospects. The propagation of the body waves mainly takes part in the inner part of the body and it also illuminates the deep geological target. The propagation of the seismic waves takes place in more than one way which are known as the wave bodies and the surface waves. Love-wave Motion: It is a type of motion in which the surface waves move parallel to the surface of the earth and perpendicularly to the direction in which they propagate.

This motion produces two components of motion in the direction of propagation i.e. Rayleigh-wave Motion: It is a type of motion in which the movement in the surface is in an elliptical way. The speed of S-waves is 1.7 times slower than P-waves and it produces vertically and horizontally on the ground surface. S-wave Motion: It is also known as the secondary waves which oscillate the ground in a perpendicular direction. P-wave Motion: It is known as the primary body wave and also the first seismic wave which can be detected by the seismographs and this motion can perform its movement through both the solid and the liquid rock. There are mainly 4 types of waves which includes P-wave Motion, S-wave Motion, Rayleigh-wave Motion, Love-wave Motion It is mainly an elastic wave that is generated by an impulse and this impulse is created by earthquakes and explosions. Seismic waves are also caused by volcanic eruptions, avalanches, landslides, huge explosions, and also sometimes by the rushing rivers. The production of seismic takes place by all of a sudden movement in the materials which are within the earth which includes a slip along with a fault which is produced during an earthquake. Seismic stations which are situated within 200 km of a continental earthquake report the time which travels which increases regularly with the distance to the source. Causes of Seismic Discontinuitiesĭue to the sudden jump in the seismic in the velocities caused by seismic which takes place around a boundary is known as seismic discontinuities. This is also known as the boundary between the outer part of the core which is known as the outer core and the mantle. The part which is just lower to this P-wave velocity is known to be less than 30% and just above it, the S-waves are completely reduced.
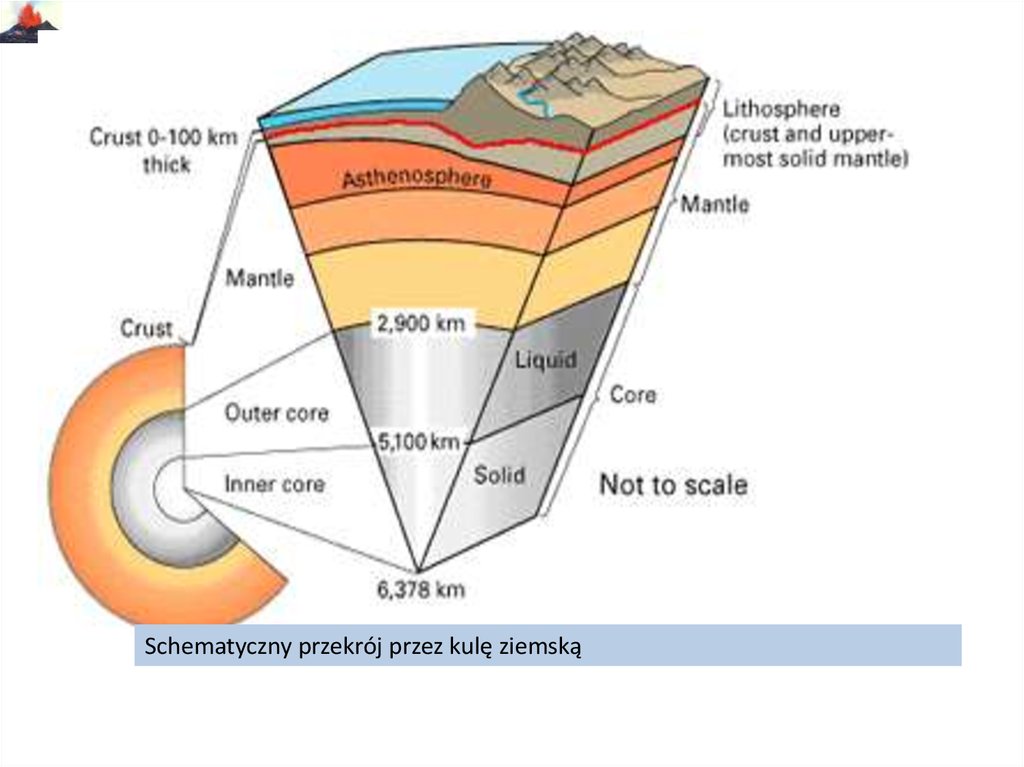
The strongest part of the Seismic Discontinuity is seen on the graph which represents velocity vs depth which is known to be situated in a depth of around 2900 km.
#Seismac discontinuity series#
It also gives us knowledge about the interior part of the earth which consists of a series of concentric shells which contain the outer crust, a mantle, an outer core of the liquid, and a solid inner core. It also helps us to know how the waves travel and in which direction the waves are traveling. The best way to know different types of Tectonic activity in the crust of the Earth is through Seismic waves and it also helps us to know where the epicenter of the earthquake is located. Seismic Discontinuity Advantages of Seismic waves reading In geology the word “discontinuity” is used for a surface at which seismic waves change velocity. A discontinuity is mainly recognized as any type of mechanical break with the big pieces of rocks and it also includes joints, weak Jones, and faults. Seismic discontinuities are mainly produced by the seismic waves and there comes an abrupt behavior which is mainly caused due to physical and the chemical properties in that place but the other places surrounding the place are normal and there is no abrupt behavior in those places.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
